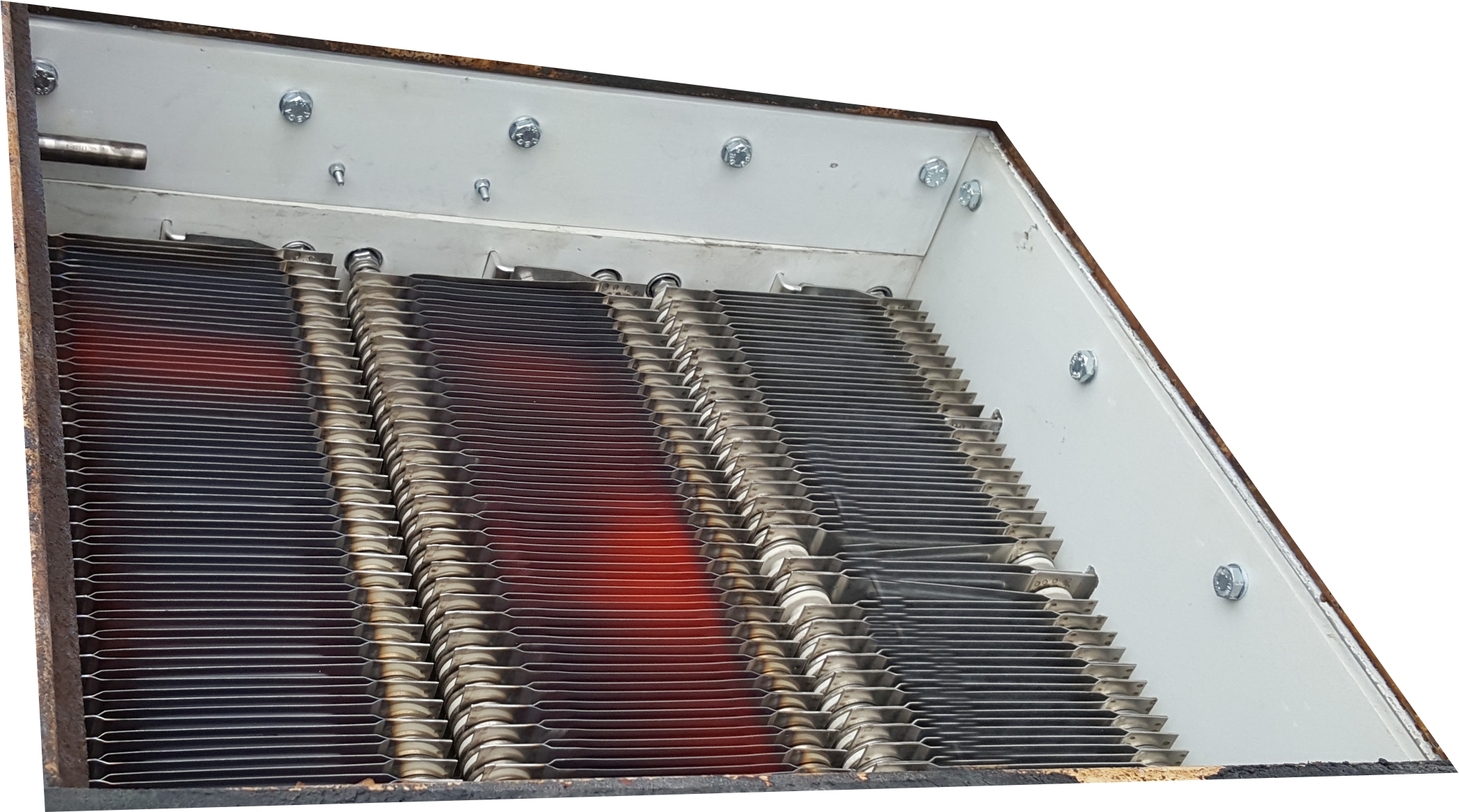
Power Resistors in Railway Vehicles
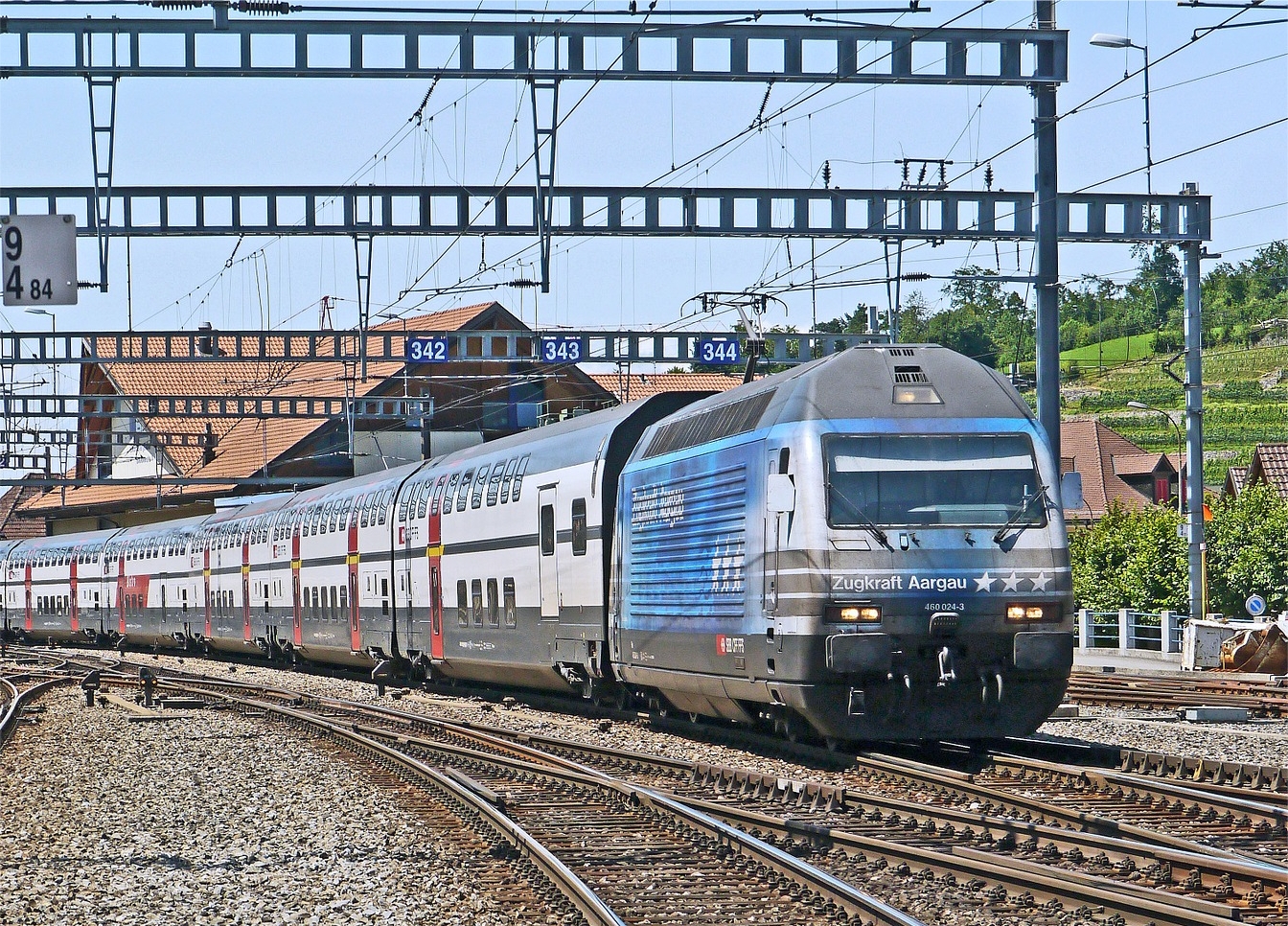
Consuming excess energy is the primary function of resistors in the power train circuit of a rail vehicle. Power resistors have a wide range of applications in rail vehicles, such as assisting the braking effort without causing mechanical wear and preventing over-voltages on converter switches.
The physical conditions inherent to railways require power resistors to be more robust, rugged and reliable than the conventional resistors most often used in the industry. EN 60322 is the main standard for dynamic brake resistors, defining the technical design and test challenges specific to railway operational conditions. There are further standards relating to vibration, insulation, etc., which specifically address the railway conditions referred in EN 60322.
The type of rail vehicle is the decisive factor in design as well as test guidelines when selecting power resistors for rail vehicles. This is due to the fact that rail vehicles are typically custom-designed in regards to propulsion power, total passenger count, and operational speed limits. Therefore, the resistor requirements for each vehicle will often be different.
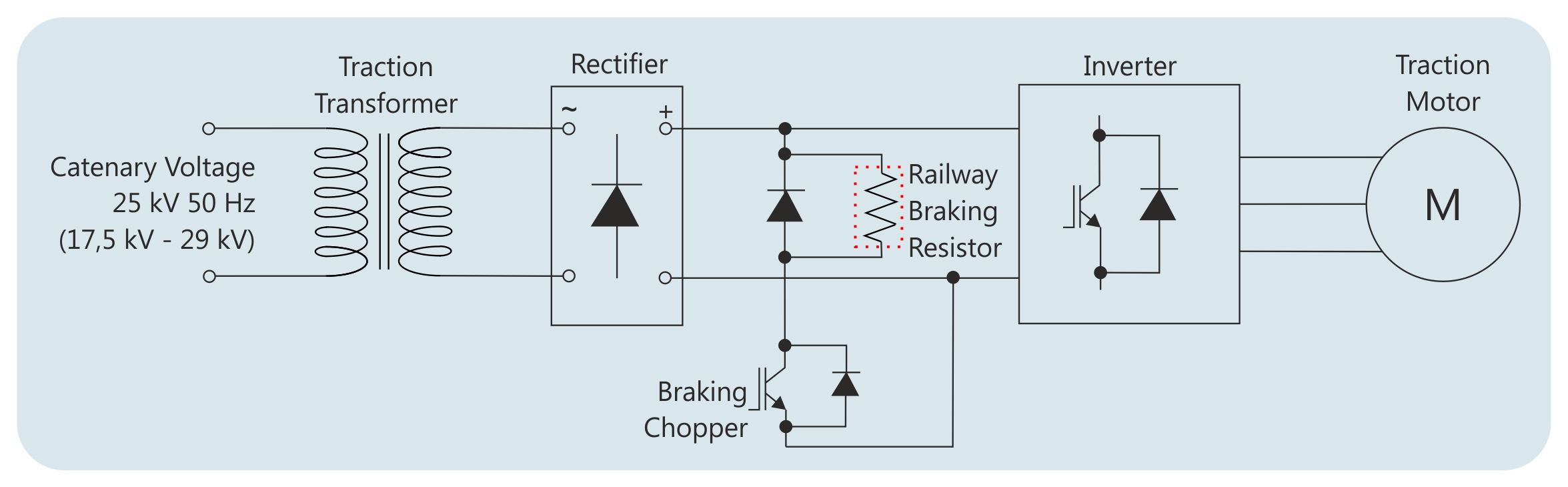
Most modern rail vehicles are equipped with propulsion power electronics that have the ability to feed the braking energy back to catenary. In mass transit networks such as metros and tramways; catenary power supplies do not have sinking ability; they are unable to intercept regenerative energy and transfer it to the grid. This is due to the circuit structure of one-quadrant operation capable, diode-based, power electronics. Therefore, braking rail vehicles via power resistors is safest for use in light duty rail transport such as metros and tramways.
In contrast to public transport railway networks; mainline networks such as intercity passenger trains or heavy freight logistics usually have catenaries with the ability to provide energy flow from grid to trains, or vice versa. Concerning the mainline railway vehicles; power resistors are mainly used in diesel-electric locomotives. Additionally, electric locomotives which do not have bi-directional energy flow must use power resistors to utilize regenerative braking.
Standards for Railway Resistor Applications
- IEC 60322 : 2001 Railway applications - Electric equipment for rolling stock - Rules for power resistors of open construction.
- IEC 61373 : 2010 Railway applications - Rolling stock equipment - Shock and vibration tests.
- EN 50124-1 : 2001 Railway applications. Insulation coordination. Basic requirements. Clearances and creepage distances for all electrical and electronic equipment.
Dynamic Braking Resistors in Public Transport Rail Vehicles
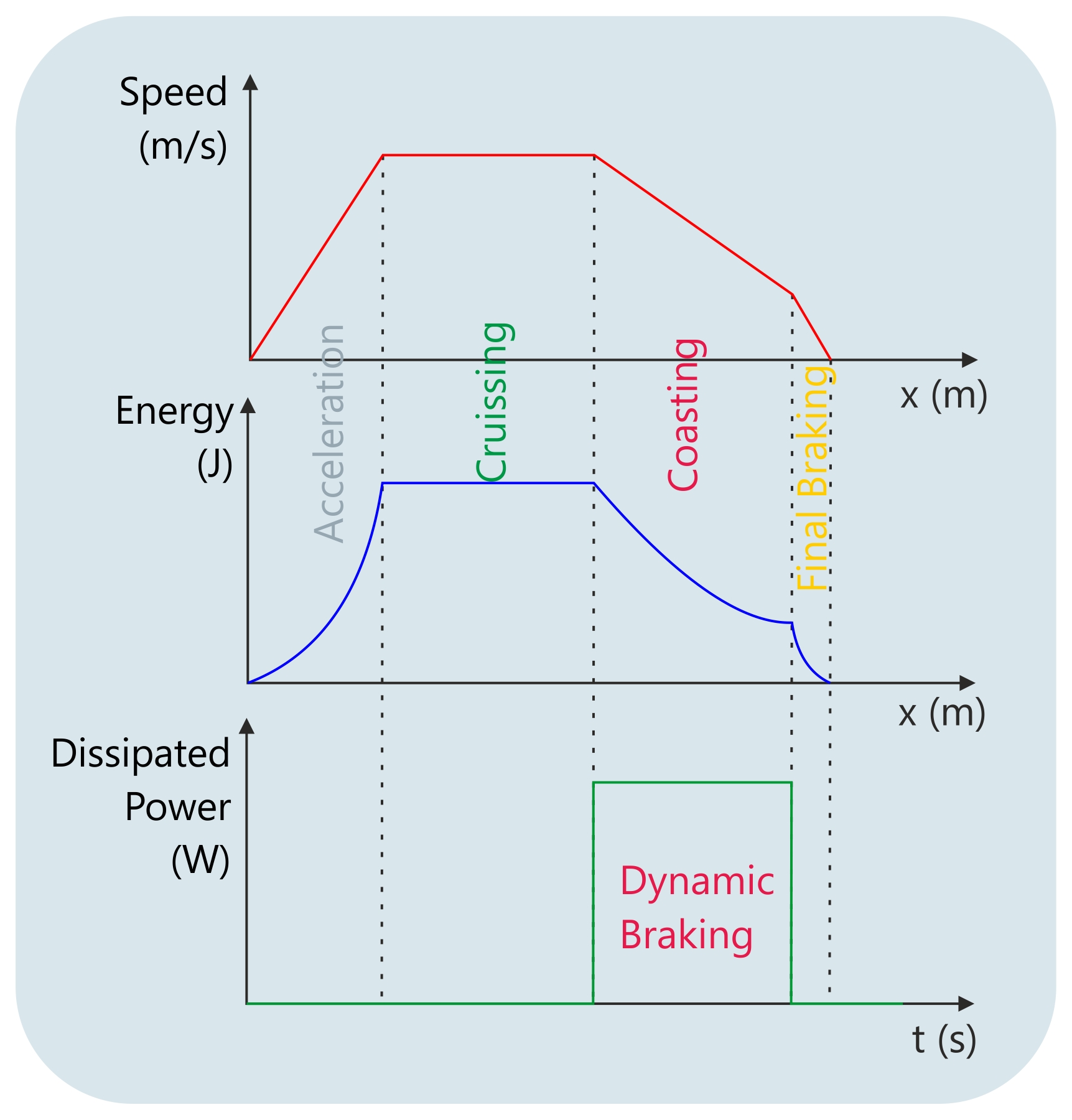
Rail vehicles used in public transport networks are operated in accelerate/decelerate drive cycles between stations. The propulsion energy flow is from the catenary to traction motors and then from traction motors to converter side. The direction of energy flow periodically changes between the stations. In a service life of a metro or tramway vehicle; public transport rail vehicles have thousands, maybe millions of times of acceleration and deceleration phases. Thus, it is critical to use regenerative braking through the deceleration phase in order to extend the lifespan of mechanical brakes. Power resistors are the key components in order for regenerative braking to be successfully applied under all conditions of catenary voltages. Additionally, dynamic braking resistors have lower wear-and-tear than friction braking resistors.

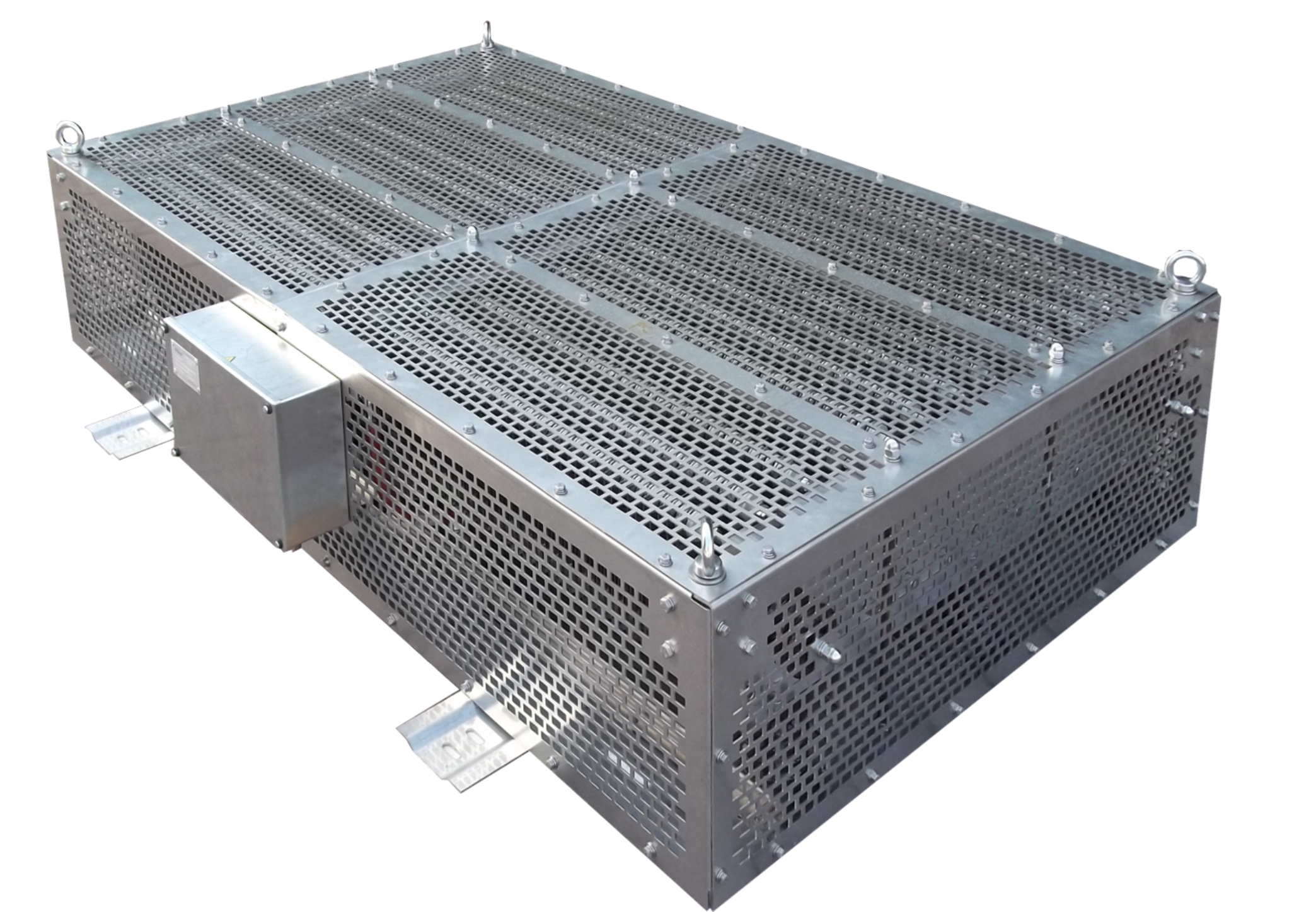
Braking resistors are designed according to braking power and time, isolation requirements, mounting place, and cooling method. Railway braking resistors can be installed on the vehicle roof, under the vehicle or in special compartments. Natural air cooling or forced air cooling methods can be used for cooling down the braking resistors.
Features of Power Resistors Utilized in Public Transport
- Negligible ohmic value change in case of sudden temperature rise of resistive elements
- Highly robust mechanical structure against vibrations
- Long life against thermal cycling due to the accelerate/decelerate phases
Dynamic Braking Power Resistors in Heavy Rail Vehicles
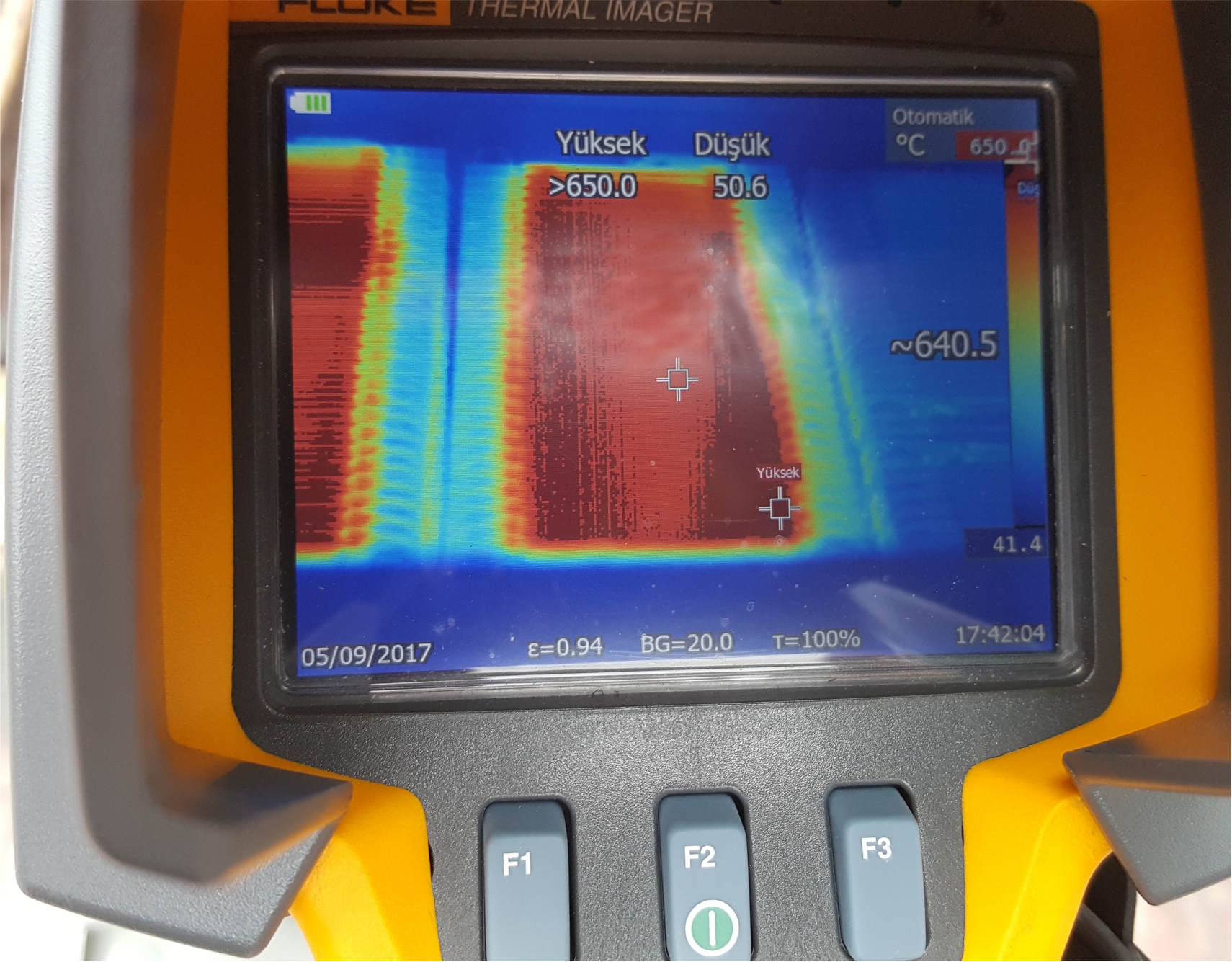
Braking is not a fluctuating event in heavy rail vehicles. Acceleration and deceleration is highly dependent on the slope of the railway. Freight locomotives may transport thousands of tonnes of loads from seaports to hills or down hills to the seaports. Thus, the braking resistors are key components for the durability and longevity of mechanical brakes and need to have a continuous braking profile for long durations. Power resistors used in heavy rail vehicles must utilize a strong mechanical structure capable of performing at high temperatures. Additionally, so as not to degrade the braking power of locomotives when the resistors are at high temperatures, it is crucial that resistance change should be kept to a minimum during temperature rises.
Features of Power Resistors Utilized in Heavy Rail Vehicles
- Negligible ohmic value change in case of sudden temperature rise of resistive elements
- Continuous operation at high temperatures
- Highly robust mechanical structure against vibrations
Crowbar Resistors, Heaters
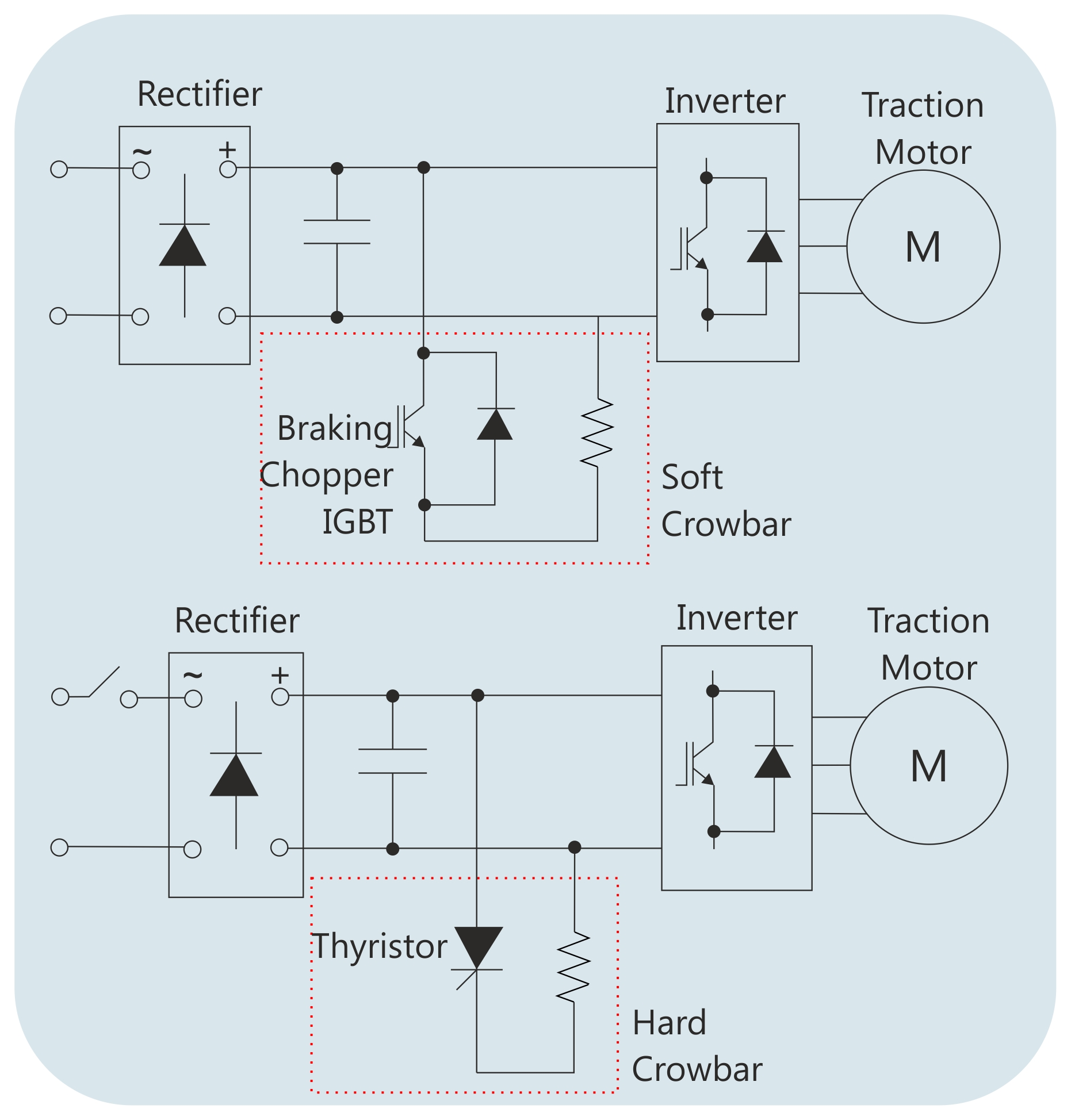
In the main, crowbar resistors protect the traction converter power electronic switches from highly damaging excessive over-voltages. There are two types of crowbar:
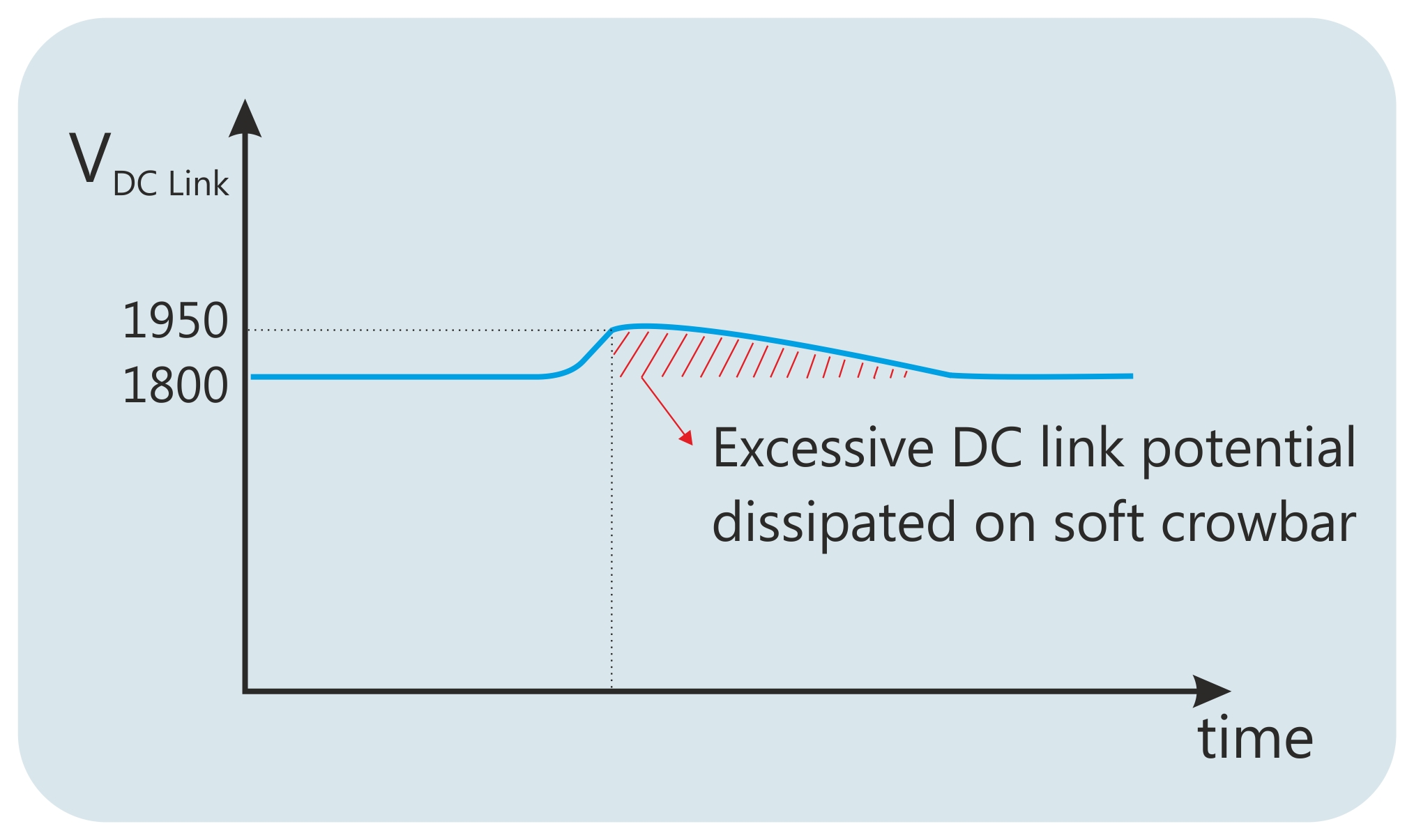
1. Soft Crowbar : a soft crowbar is utilized to reduce the DC link voltage in case of DC link over-voltages. A soft crowbar resistor is connected to the DC link with a serial connected IGBT.
2. Hard Crowbar : a hard crowbar is utilized to force the high-speed circuit breaker to open in order to protect converter parts from massive damage caused by over-voltages. A hard crowbar resistor is always connected to the DC Link with a serial connected thyristor.
Crowbar resistors are designed to dissipate high energy in a very short time period. While sizing the electrical ratings of crowbar resistors; input front-end converter component ratings, HSCB ratings and the energy stored in the DC link capacitance should be used in the calculations.

Features of Crowbar Resistors Utilized in Traction Converters
- Very compact mechanical structure
- Highly reliable mechanical structure against sudden temperature variations
- Highly robust mechanical structure against vibrations
- Negligible ohmic value change in case of sudden temperature rise of resistive elements
Wagon Heater Resistors
Wagon heating resistors are employed either in a regenerative braking path or as a stand-alone on public rail transport vehicles. Wagon heating resistors do not only function as resistors. They also provide double protection devices and diagnostic capabilities.
Protections Used in Heating Resistors
- Over-heating protection of heater elements
- Excessive heating of wagons
- Protection against fan faults
- Protection against power supply faults of sensor supplies
- Redundant circuit breaker against contactor failure
- Both switching on/off the heating resistor's state signals are transmitted to train control system
Hilkar wagon heating resistor solutions are designed and manufactured in the scope of EN 60322 Standard. Sub-components used inside the heating resistors comply with EN50155 Railway Standards.
Locomotive Testing & Trackside Resistors
Hilkar designs and manufactures custom design load banks for the testing of Diesel Electric Locomotives. The power train of diesel electric locomotives consists of a high-power rated diesel engine, an alternator and rectifier units. Testing units are usually connected to the DC part of diesel electric power trains. This is to test both the diesel engine, alternators and rectifier units before commissioning the locomotives.
Hilkar can provide customization in either the mechanical or electrical design concepts. Both continuous rated power and pulsating peak power inputs coming from diesel electric power trains are perfectly dissipated with the well-structured thermal design of testing units.
Features of locomotive testing units are:
- Customizable mechanic structure and packaging
- Ability to cool MWs of dissipated power
- Customer oriented solutions for the control of testing units
- Negligible ohmic value change in case of sudden temperature rise of resistive elements
Trackside resistor units are employed in public transport catenary supply grids. The voltage range of catenary supplies is defined in EN 50163 Standard. The traction converters of metro and tramway vehicles are designed in accordance with the maximum allowable catenary voltages defined in this standard.
Since the traction power supply of 750Vdc or 1500Vdc catenary public transport grids are diode based converters, their DC side voltages are not controllable. Thus, some units should limit catenary voltages in order to run the rail vehicles safely. Trackside resistors are the voltage limiters in the case of catenary supply over-voltages.
Inductive Components for Rail Vehicles
Inductive components are the critical components for both auxiliary converters and main drive power electronics systems. Inductive elements for on-board AC and DC drive systems must have a strong mechanical structure to protect against vibration and a state-of-the-art thermal design in order to have the most compact size.
Air Core / Iron Core Chokes – Reactors
In order to filter out the harmonic components of the catenary supply of converters, line chokes are used. For air core reactors, inductance is kept constant to filter out harmonics during short circuit instances.
Sine filter inductive components, customized for inverters, are usually employed in order to supply traction motors with low harmonic sinusoids.
Transformers for Auxiliary Converters
Transformers at the output stage of auxiliary converters typically supply accessory loads and the power supply of electronic circuits. Transformers for auxiliary converters require very compact design with high thermal responses in case of full-load operation in a steady state.
Standards
EN 61373 for vibration tests; IEC 60310 for the general standards of railway related inductive components.
Fire Protection Standard EN 45545
Hilkar is dedicated to serving our customers with customized solutions for on-board equipment of rail vehicles such as fire/smoke protection standard EN 45545. Hilkar has a broad range of inductive products ensuring EN 45545 both in air core and iron core reactors/transformers.